Ancient Greece

The Ancient Greeks were people who lived in the area around the Greek Peninsula between 4,000 and 2,500 years ago. They spoke the same language and worshiped the same gods but they lived in independent city-states.
City-States
In ancient times, Greece was not a country like it is today. Instead, the people were ruled by independent city-states. These city-states were sometimes allied with each other, and sometimes enemies.
A city-state included not just the main city but the villages and the countryside around the city. There were hundreds of city-states, but the most powerful were Athens and Sparta.
Greek city-states shared a language and a religion, but they had different laws, governments, and currency. Sometimes, the city-states allied together to fight a common enemy, like Persia, the ancient land in what is now southwestern Asia.
Religion
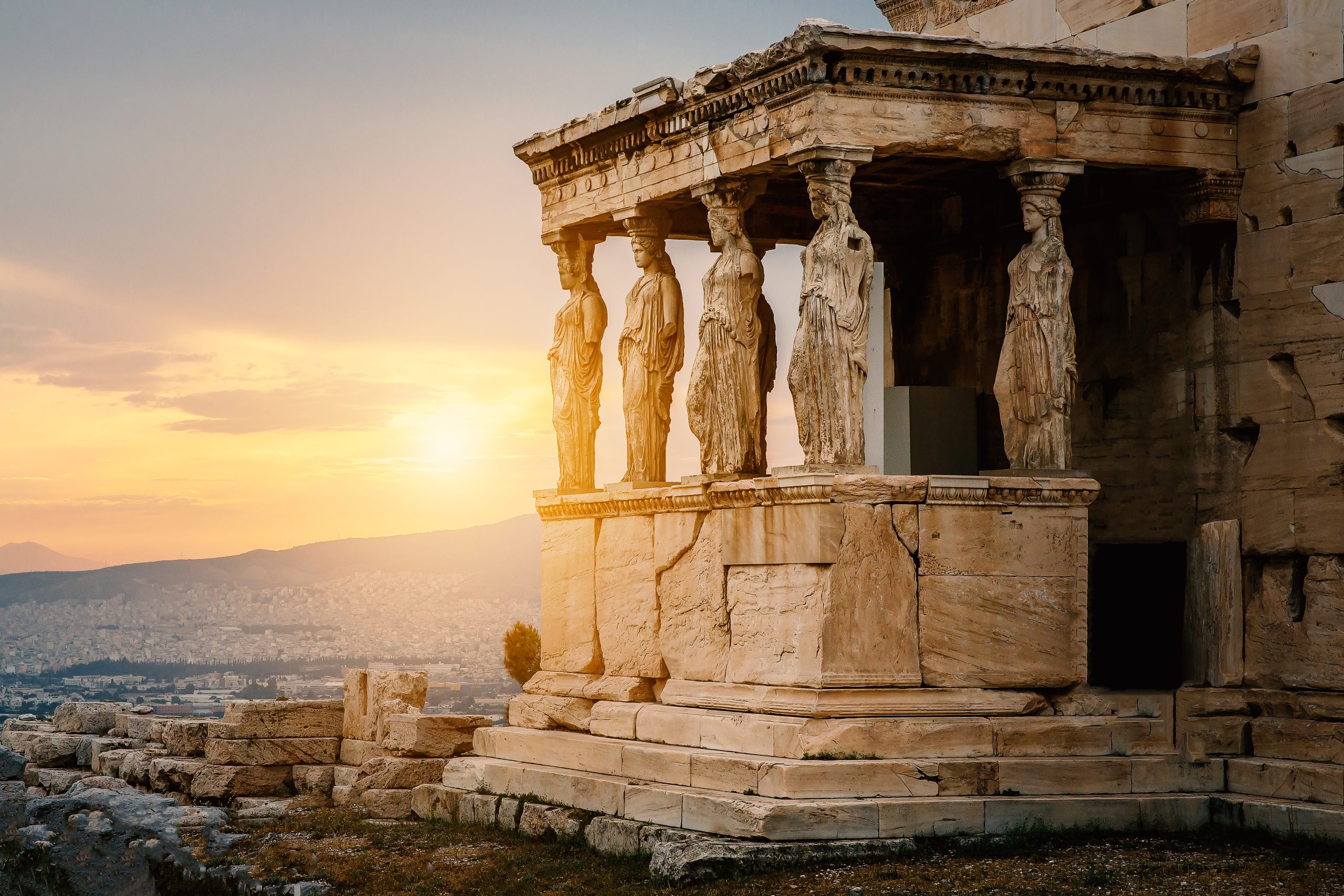
Ancient Greeks worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses as part of their everyday life. The actions of gods explained things they didn’t understand or couldn’t control, like lightning and the seasons. Cities built temples to their patron god or goddess, a place people could visit to worship. The Parthenon of Athens was dedicated to Athena, their patron goddess.
Language
While Greeks shared a common language (Ancient Greek), city-states had their own dialects (ways of speaking). They also had slightly different spellings for words, and some city-states used different letters.
The modern Greek language evolved from Ancient Greek, and the English alphabet is derived from the Greek alphabet. The alphabet is even named after the first two letters of the Greek alphabet, alpha and beta.
Time Periods
Ancient Greek history can be split into three different periods.
During the Archaic Period (750– 480 BCE) city-states were formed, the Olympics began, Homer wrote the Iliad and the Persian wars began.
The Classical Period (480 BCE – 323 BCE) is the time when philosophers flourished, democracy was instituted in Athens, and Alexander the Great conquered Persia.
The Hellenistic Period (323 BCE – 31 BCE) lasted from the death of Alexander the Great, to the annexation of Greece by the Romans. During this time, Greek culture spread across Mediterranean as well as West and Central Asia.
Legacy
Ancient Greece developed many ideas about government, art, theatre, sports, architecture, philosophy, science and math that still influence the modern world. Democracy, the Olympics, the golden ratio and the Pythagorean theorem are a few examples of ideas from Ancient Greece that are still in use today.